- A stock option is also known as an equity option.
- It will give an investor the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at an agreed price.
What is option trading?
- An option is a contract written by a seller that will convey to the buyer the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a particular asset at a specific price in the future.
- In return for granting an option, the seller will collect a payment, known as a premium, from the buyer.
- A particular asset includes a stock, commodity, ETF, and currency.
- Option contracts come with a fixed expiration date, which is usually the last Thursday of a calendar month.
- When the date of expiry arrives, the contract will expire, and eventually its value will become zero.
- Options do not obligate the buyer or seller to honor the contract.
- Options trading in the stock market implies you will not own the shares until you exercise the option.
- When you invest in the stock, you will become a part-owner of the company.
- However, when you trade options, you will simply express your desire to own the shares of the company on a specified date but not own them in real life.
Understanding options trading:
- With options trading, an investor or trader can buy or sell stocks, ETFs, and other securities at a certain price and within a certain date.
- It is a type of trading that will offer investors fair flexibility to not purchase a security at a certain date or price.
How does option trading work?
- When the trader purchases or sells an option, they will have the right to apply that option at any point in time, but before the expiration date.
- Merely buying or selling an option will require an individual to exercise the option at the time of expiration.
- Due to this strategy, options are treated as derivative securities.
Strategies in options trading
There are many strategies in options trading.
They are as follows:
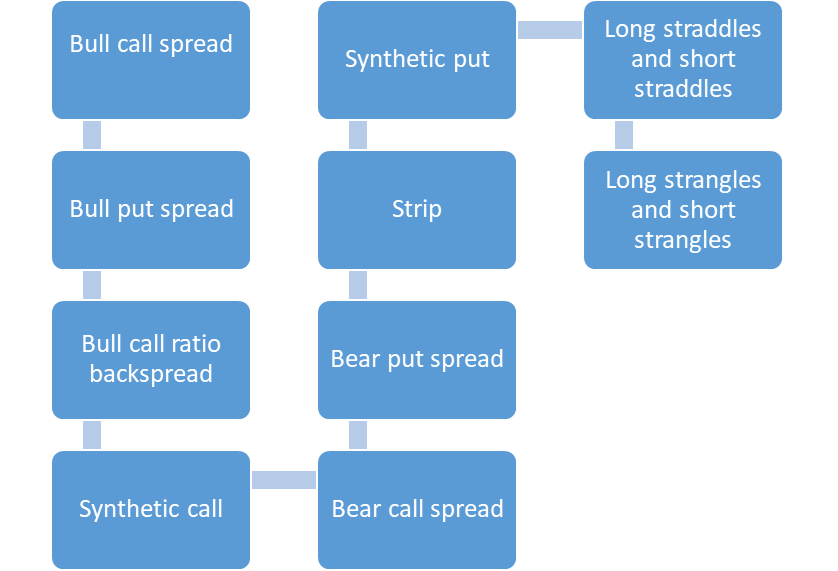
Bull call spread:
- The bull call spread comes under the debt spread strategy.
- A bull call spread is made by purchasing one call option and concurrently selling another option with a lower cost and a higher strike price.
- Both of them have the same expiration date.
- This is considered to be the best option-selling strategy.
Bull put spread:
- When the trader believes that the price of the stock will increase moderately shortly, they will use the bull put strategy.
- This strategy falls under the credit spreads strategy.
- In simple terms, this spread will mean selling a put option and purchasing a put option with a lower strike.
- This strategy is considered to be a great option-buying strategy.
Bull call ratio back spread:
- A trader will need to be bullish to make this trade.
- Being marginally bullish will not work for this trade.
- The main loss here happens in the direction in which the trader hopes the trade will move.
- This back spread consists of two parts, as follows:
- Selling one or more out-of-pocket or out-of-pocket calls and purchasing two or three calls that are less expensive than the call that was actually sold.
Synthetic call:
- An investor will purchase and hold a share to start with a synthetic call, which is also known as a synthetic long call.
- To hedge against the decline in the price of the stock, the investor will buy a money-put option for the same stock.
Bear call spread:
- When one feels that the market is largely bearish, he might use a double-options trading strategy, which is termed a bear call spread.
- Under this method, the trader will sell a short-term call option while buying a long-term call option with the same commodity and time frame as the expiration date but with a higher strike price.
Bear spread:
- A trader will use a bear put spread when they predict that the price of the asset will slightly decline.
- Purchasing put options and selling the same number of puts on the same asset with the same expiration date at a lower target is a bear put spread.
Strip:
- When the investor is bullish on volatility and bearish on the direction of the market, they can employ this strategy.
Buying two lots of the following will be considered part of this strategy:

- The same security and expiration month are required for both options.
- Here, significant gains are possible when the underlying asset makes a significant move at expiration by moving in the direction of loss.
Synthetic put:
- An investor who is selling short and purchasing a call is considered to be using this strategy, which is equivalent to buying a put option.
- This strategy mimics a long put option by holding both a short stock position and a long call option on the very same stock.
Long straddles and short straddles:
- A long straddle is the easiest market-neutral trading strategy to execute.
- The direction of the movement after this has been applied has no bearing on profit or loss.
- In a long straddle, a trader will purchase a long call and a long put.
- A short call or a short put will be purchased with the same asset, expiration date, and strike price, which becomes part of the short straddle option.
Long strangles and short strangles:
- The long strangle will be utilized when the trader anticipates high volatility in the underlying stock shortly.
- This is a method with low risk and high payoff potential.
- The short strangle aims to increase the profitability of the trade for the option seller.
Participants have the following options:
The main participants in the options are as follows:
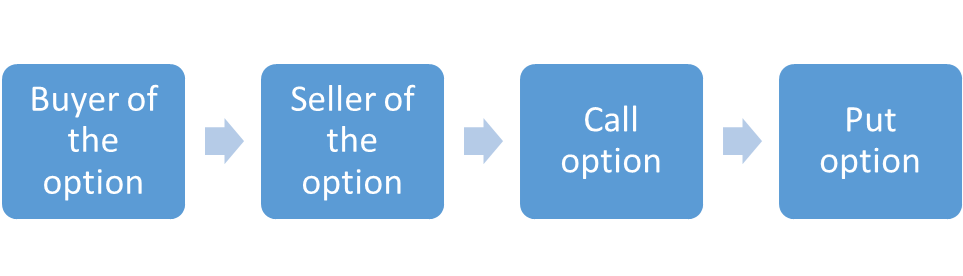
Buyer of the option:
The one who pays the premium to buy has the right to exercise his option against the seller or writer.
Seller of the option:
He is the one who will receive the premium of the option and is also obliged to buy or sell the asset if the buyer exercises the option.
Call option:
A call option is an option that will provide the holder with the right but not the obligation to buy an asset at a set price before a certain date.
Put option:
A put option will offer the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an asset at a set price before a certain date.
Notable terms in options trading:
The main terms in options trading are as follows:
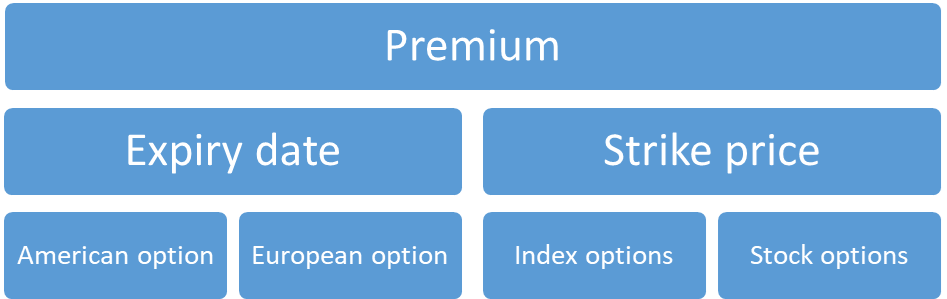
Premium:
The price that the option buyer will pay to the option seller.
Expiry date:
The date that is specified in the options contract is the expiration or exercise date.
Strike price:
The price at which the contract is entered.
American option:
The option will be exercised at any date until the expiration date.
European option:
The option can be exercised only on the expiration date.
Index options:
Examples of these options are nifty options and bank nifty options.
Stock options:
These are the options on individual stocks where the contract will give the holder the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specific price.
Conclusion
Option trading is the most versatile trading and will provide a trader with ample opportunity in each market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1) How do I do option trading?
You will first need to open an options trading account and then choose which option to buy or sell.
Q2) Are options better than stock?
Options can be a better choice when you limit your risk to a certain amount.
Q3) Which trading style is best for beginners?
Day trading is the best for beginners.
Q4) Is 5000 rupees enough to start trading?
Yes, you can start trading with even Rs. 5,000.
Q5) Is trading options gambling?
It is generally regarded as a legitimate part of the financial market, rather than gambling.
About Us:
Nifty Trading Academy is our academy, where we teach you about the stock market as well as technical analysis. We also upload blogs for the same and provide live market trading.
