- Money markets are for meeting short-term liquidity requirements, whereas capital markets will cater to long-term investment requirements.
- The money markets are more liquid and less risky than the capital markets.
What is the money market?
- A money market is a financial market for liquid, short-term securities that have a maturity tenure of less than a year.
- This market will facilitate the quick borrowing and lending of funds.
- This will also cater to the immediate cash requirement in the economy and mobilize funds from different sectors of the economy.
- In simple words, money markets will offer a platform where businesses and governments can obtain short-term funding to meet immediate liquidity needs.
What is a capital market?
- A capital market is a financial market for long-term investments.
- Long-term equity in debt-backed securities such as stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds is bought and sold in this capital market.
- Capital market investment instruments will come with a maturity period of more than a year.
- These markets will provide a platform for companies and governments to raise funds for long-term projects.
- Capital markets will help to mobilize the savings for the investment and also fund long-term projects through trades and transactions on the exchanges.
Key Differences Between the Money Market and The Capital Market
There are several differences between both markets..
The following table will highlight the differences:
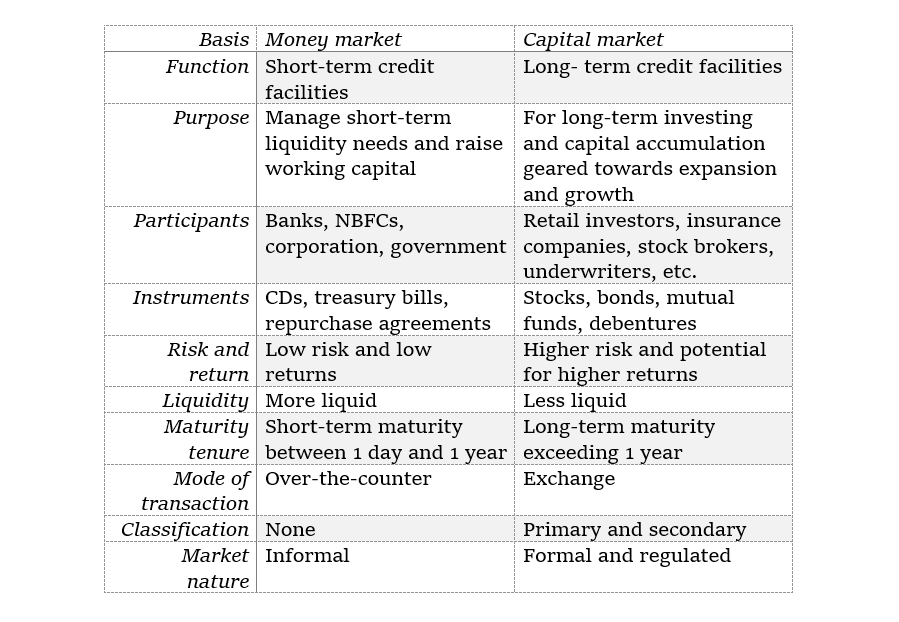
Money Market vs. Capital Market: Differences with Examples
Definition
- A money market is a short-term lending system that will allow businesses to raise working capital for their day-to-day operations.
- A capital market is geared towards long-term investment, where companies will issue stocks and bonds to raise capital and expand their businesses.
Maturity of instruments
- The maturity period of money market instruments will range from 1 day to 1 year.
- Capital market instruments are long-term investments that have a maturity period exceeding 1 year.
- Most of the capital market instruments might not even have a stipulated maturity date.
Purpose served
- Money market instruments are designed for short-term borrowing and lending.
- Firms will borrow a small percentage of their overall asset base so as to meet immediate cash flow requirements, such as working capital demands.
- Apart from these, capital market investments are made for long-term growth, business expansion, and capital formulation.
Market nature
- Money markets are generally informal markets.
- Capital markets are formal and regulated.
Instruments involved
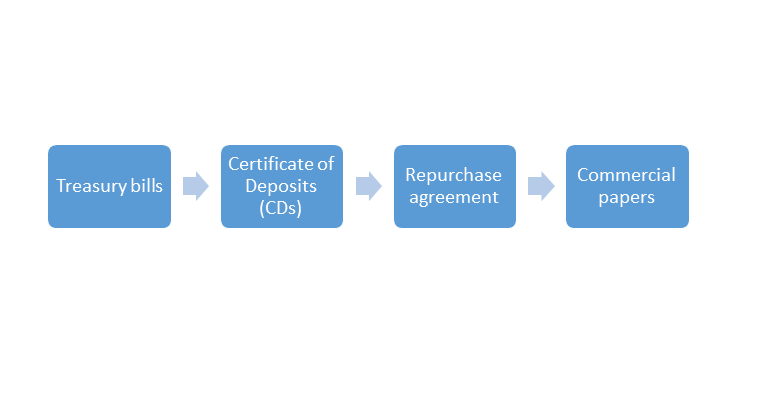
- Money market instruments will include Treasury bills, commercial papers, certificates of deposit (CDs), repurchase agreements, and call and notice money.
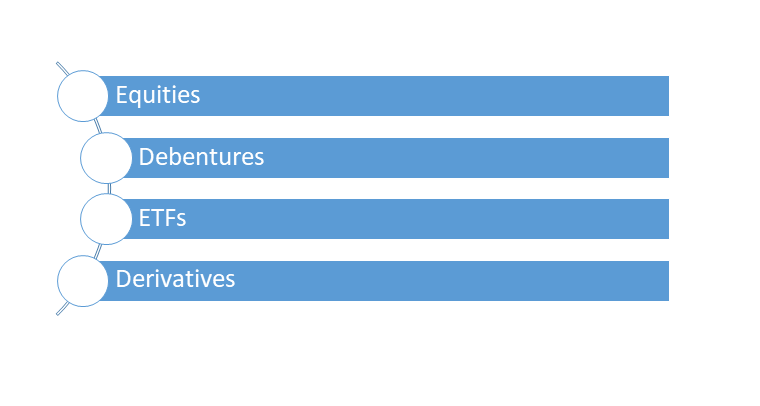
- Capital market instruments will include stocks, bonds, mutual fund schemes, and ETFs.
Investor Types
- The key players in the money market are banks, NBFCs, corporations, and the government.
- These participants will either wish to park their funds for the short term or are also looking for short-term loans so as to meet their immediate cash flow requirements.
- The most common participants in the capital market are the companies selling stocks and bonds, retail investors buying securities, the government issuing bonds, institutional investors, and investment banks.
Market liquidity
- Money market instruments such as CDs have a shorter maturity and can also be converted into cash as compared to capital market instruments such as stocks and bonds.
Risk involved
- Risk is considered to be an important element of the money market as compared to the capital market.
- The short-term duration as well as the high liquidity of the money markets will make them less risky than the long-term and volatile capital markets.
Functions served
- The money market will aim to provide short-term liquidity to the economy.
- The capital market will aim to help raise long-term capital for growth and development.
Return on investment achieved
- Money market returns are generally lower but more stable than in the capital markets.
- Long-term capital market investments will pose higher risks, which will also bring you better returns.
Examples of money market instruments
Money market instruments have a lot of instruments in them.
They are as follows:
Examples of capital market instruments
There are several examples of capital market instruments.
They are as follows:

Advantages of investing in the money market
There are several advantages to investing in the money market.
They are as follows:
- These instruments can be easily converted into cash, thereby ensuring easy liquidity for the investor.
- They are low-risk investments that focus on short-term debt, which also makes them relatively safer than equity stocks.
- Money market instruments such as CDs offer fixed interest rates, which will ensure stable and predictable returns.
- Investors will also invest in money market instruments through banks and NBFCs, which will make them easy to acquire.
Advantages of investing in the capital market:
There are several advantages to investing in the capital market.
They are as follows:
- They are a secured trading space, as capital markets in India are regulated by SEBI.
- They have the opportunity to maximize returns with an investment in high-yielding securities such as equity stocks.
- Investors will be able to choose from a wide range of investment options to curate a diversified portfolio and also spread the overall investment risk.
- Investment in all the dividend-paying instruments will also allow regular and steady cash flow for the investor.
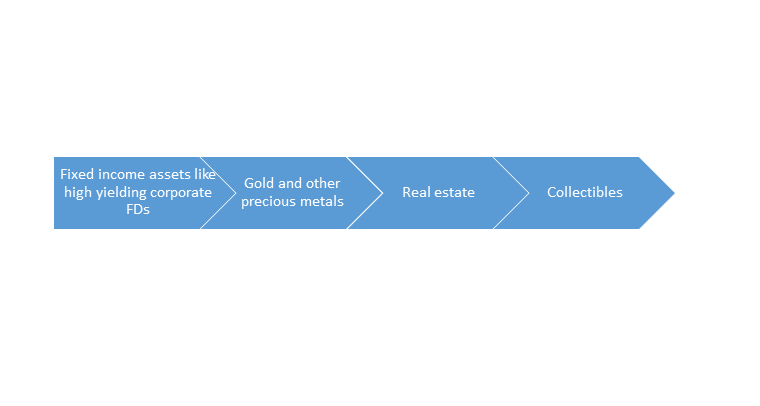
Alternatives to the money market and the capital market:
A diversified portfolio will work best for hedging risk that is associated with market volatility.
Hence, if you wish to diversify your portfolio beyond the money and the capital market, then you can consider the following options:
Conclusion
Before jumping into the money and capital markets, you should look for the pros and cons of both markets and then invest accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1) What is the main difference between the money market and the capital market?
The main difference between the money market and the capital market is the duration of the investment and the risk component.
Q2) What is the difference between the financial market and the capital market?
A financial market is a place where trades related to financial assets will take place, whereas a capital market is one where companies and the government will raise long-term capital.
Q3) What is the difference between the equity and money markets?
An equity market will trade in stocks, whereas the money market will handle all the short-term investments.
Q4) What is the most common example of the money market?
The money market will include Treasury bills, CDs, money market mutual funds, commercial papers, and repurchase agreements.
Q5) What is an example of the capital market?
The main example of the capital market is the BSE, or Bombay Stock Exchange, where stocks, bonds, and other long-term securities are traded.
About Us
Nifty Trading Academy is our academy, where we teach you about the stock market as well as technical analysis. We also provide live trade sessions and upload blogs for them.
